The Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptor Delta Regulates Developmental Neurogenesis
Fecha
2020Autor
Cancino, Gonzalo I. [Univ Mayor, Fac Ciencias, Ctr Integrat Biol]
Aranda-Pino, Begoña [Univ Mayor, Fac Ciencias, Ctr Integrat Biol]
Cornejo, Francisca [Univ Mayor, Fac Ciencias, Ctr Integrat Biol]
Tomita, Hideaki
Woodard, Cameron L.
Rioseco, Constanza C.
Neel, Benjamin G.
Alvarez, Alejandra R.
Kaplan, David R.
Miller, Freda D.
Ubicación geográfica
Notas
HERRAMIENTAS
Acceda a títulos restringidos
¿Cómo descargar?Resumen
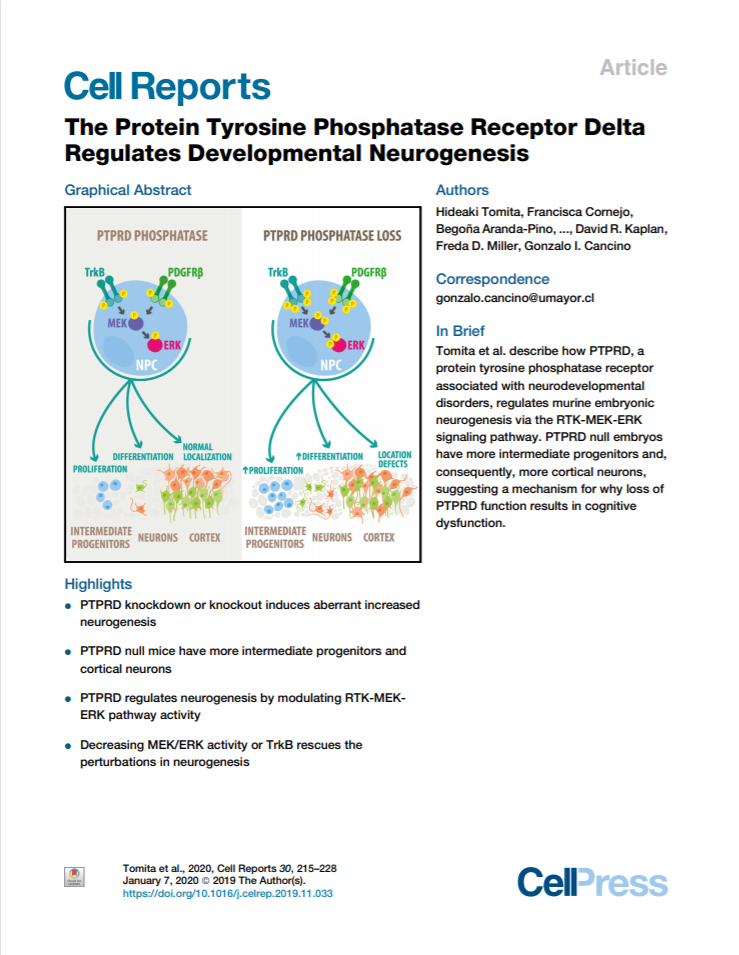
PTPRD is a receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase that is genetically associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Here, we asked whether Ptprd mutations cause aberrant neural development by perturbing neurogenesis in the murine cortex. We show that loss of Ptprd causes increases in neurogenic transit-amplifying intermediate progenitor cells and cortical neurons and perturbations in neuronal localization. These effects are intrinsic to neural precursor cells since acute Ptprd knockdown causes similar perturbations. PTPRD mediates these effects by dephosphorylating receptor tyrosine kinases, including TrkB and PDGFR beta, and loss of Ptprd causes the hyperactivation of TrkB and PDGFR beta and their downstream MEK-ERK signaling pathway in neural precursor cells. Moreover, inhibition of aberrant TrkB or MEK activation rescues the increased neurogenesis caused by knockdown or homozygous loss of Ptprd. These results suggest that PTPRD regulates receptor tyrosine kinases to ensure appropriate numbers of intermediate progenitor cells and neurons, suggesting a mechanism for its genetic association with neurodevelopmental disorders.
URI
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.033http://repositorio.umayor.cl/xmlui/handle/sibum/6498
Coleccion/es a la/s que pertenece:
Si usted es autor(a) de este documento y NO desea que su publicación tenga acceso público en este repositorio, por favor complete el formulario aquí.